How to Optimize Your Omega-3 and Omega-6 Intake
People are increasingly concerned about their health since the pandemic. People appear to be more conscious of what they eat and are seeking a healthier lifestyle. There are many ways to stay healthy, and the best way for each one varies. However, there are some general tips that can help anyone who wants to be healthy. One of these is maintaining a healthy Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio in our bodies. In this article, we will discuss why having an optimal Omega-3 Omega-6 ratio in your body is important and how we can achieve it.

Health Benefits of Omega-3 and Omega-6
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play an important role in our body. They can be found in both plant and animal sources. Because the body cannot produce them, they must be obtained through diet. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to help prevent heart disease, mental disorders like depression as well as chronic inflammation.
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential for human health as well, and they are mainly found in oils, nuts, and seeds. Omega-6 is also found in different types of vegetable oils. Omega-6 fatty acids help to maintain healthy skin, brain function, and blood sugar levels. Omega-6 fatty acids are also involved in the production of prostaglandins, which are hormones that play important roles in regulating many body functions. Prostaglandins help regulate blood pressure and heart rate, and they can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke[2].
What is the Optimal Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio?
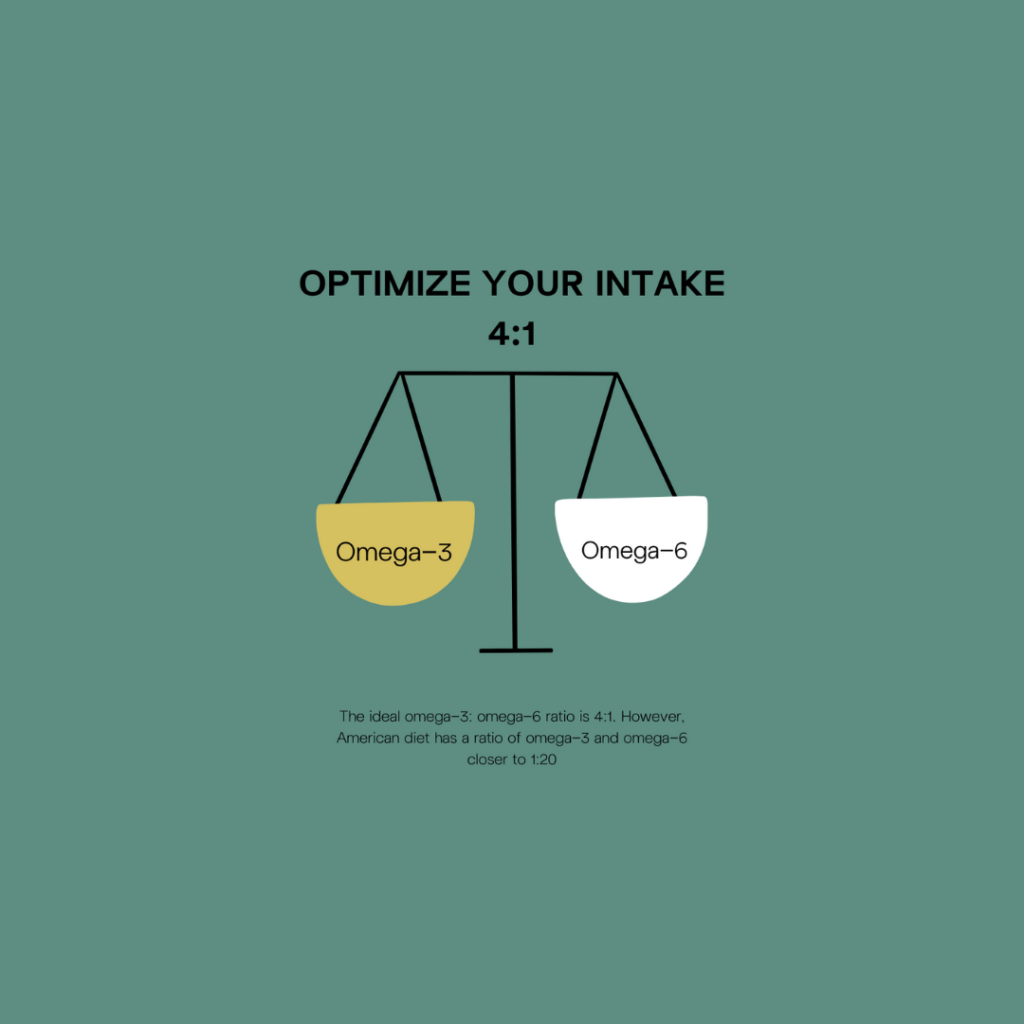
The ideal omega-3: omega-6 ratio is 4:1[3]. However, the American diet has a ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 closer to 1:20[4]. One of the reasons for this imbalance is that we consume too many processed foods that are high in omega-6 fatty acids. This imbalance can lead to inflammation, obesity, cancer, diabetes, and heart disease

In general, scientists believe omega-6 fatty acids are pro-inflammatory, whereas omega-3 fatty acids are anti-inflammatory[6]. At normal levels, omega-6 fatty acids can help to raise good cholesterol (HDL) and lower bad cholesterol (LDL). However, a diet high in omega-6 fatty acids, on the other hand, can increase bad cholesterol as well as inflammation, increasing the risk of many chronic diseases. Sometimes your body produces too many prostaglandins, which causes unwanted and harmful inflammation. Too many prostaglandins can cause vasodilation, induce fevers, and stimulate cells involved in allergic reactions[7]. That is why we need to balance the consumption of these two fatty acids and limit our omega-6 intake.
The Advantages of an Optimal Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio
There is a growing body of scientific evidence that suggests a good omega-3 to omega-6 ratio is important for overall health.
-
Reduces risk of chronic disease
A healthy omega-3 to omega-6 ratio can help to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, arthritis, and many other chronic diseases[8]. This is due to the fact that omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and may be useful in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
-
Benefits mental health
A good omega-3 to omega-6 ratio can also help to improve mental health and cognitive function. In fact, a study found that people who had a high omega-3 to omega-6 ratio had a reduced risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease[9].
-
Promotes fetal development
Adequate omega-3 fatty acid consumption is critical during pregnancy because they are essential building blocks of the fetal brain and retina. Researchers also discovered that infants born to mothers with higher blood levels of the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) at birth had advanced attention spans well into their second year of life[10].
How to Reach the Optimal Ratio of Omega-3 to Omega-6?
Here are some easy tips for getting the right ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 in your diet:
-
Eat enough omega-3.
Eating enough omega-3 can be difficult, especially if you have trouble coordinating your appetite and eating habits with the recommended daily intake of food. Others may struggle to understand nutrition labels or are unfamiliar with what different food is offering. Omega-3s are found in seal blubber and oily fish like salmon or tuna. Consuming more of these foods will assist in balancing the omega-3: omega-6 ratio in your body. Omega-3 supplementation, such as seal oil or fish oil, is an option to consider for those who do not consume the foods listed above on a regular basis.
-
Avoiding processed seed and vegetable oils as well as the processed foods
In general, you can reduce your omega-6 intake by consuming fewer processed and fast foods, as well as polyunsaturated vegetable oils (corn, sunflower, safflower, soy, and cottonseed, for example). Unhealthy foods that are high in omega 6 fats include processed snacks, fast foods, cakes, cream, and cured meats. Stopping eating those food is a wise decision. You can use Extra-virgin olive oil in cooking and salad dressings. Butter, coconut oil, lard, palm oil, and olive oil are all low in omega-6 fatty acids[11].
-
Improve omega-3 absorption with seal oil
There are several ways to optimize omega-3 absorption, including taking meal with a high level of healthy fatty acids, and avoiding alcohol[12]. Seal oil, along with mother’s breast milk, is a rare natural source of DPA. DPA functions as a “storage depot,” allowing the body to store and access these important omega-3 fatty acids as needed[13] . DPA improves both absorption and utilization of omega-3 According to a scientific study, those who consumed seal oil had a higher total level of omega-3s in their bodies after 14 days of supplementation than those who consumed fish oil[14].

Conclusion
A balanced omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acid ratio is important for overall health. To maintain a healthy omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acid ratio, it is important to include both types of fatty acids in your diet but in a right ratio. Omega-6 supplementation is usually unnecessary unless you are treating a specific condition because the Western diet contains enough omega-6 fatty acids. Instead, you should keep an eye on increasing omega-3 intake.
By increasing your intake of omega-3-rich foods and supplements, you can optimize your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio and improve your overall health. Some good sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. However, taking seal oil is probably the most straightforward and convenient way for you to boost omega-3 levels in your body.
[1] https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/types-of-fat/omega-3-fats/#:~:text=Likely%20due%20to%20these%20effects,key%20family%20of%20polyunsaturated%20fats.
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3159200/
[3] https://riverview.org/blog/uncategorized/get-an-oil-change-improving-your-omega-6-to-omega-3-ratio/
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808858/
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808858/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20500789/
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3961086/
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12442909/
[9] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23451843/
[10] https://www.webmd.com/baby/news/20040716/pregnant-omega-3-essential-for-babys-brain
[11] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/optimize-omega-6-omega-3-ratio#:~:text=Avoid%20Vegetable%20Oils%20High%20In%20Omega%2D6&text=You%20can%20see%20that%20butter,oils%20contain%20the%20highest%20amounts.
[12] https://abcnews.go.com/Health/Healthday/story?id=4508064&page=1
[13] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22729967/
[14] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20652432/