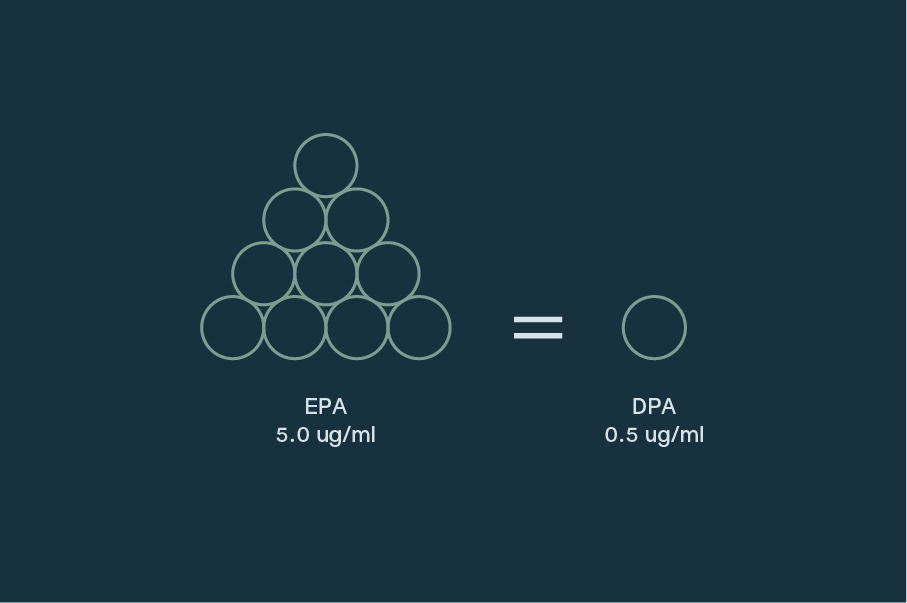
Boosts all key Omega-3’s
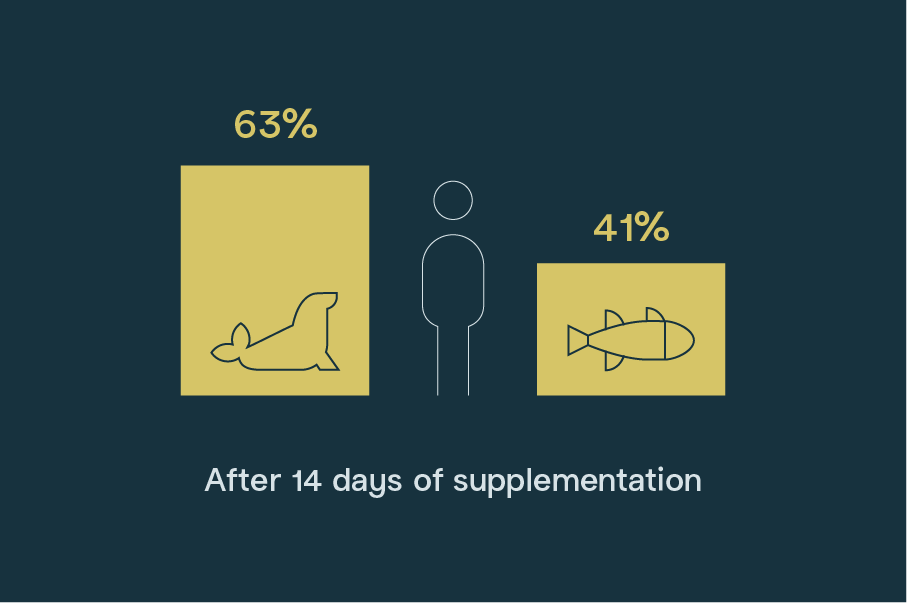
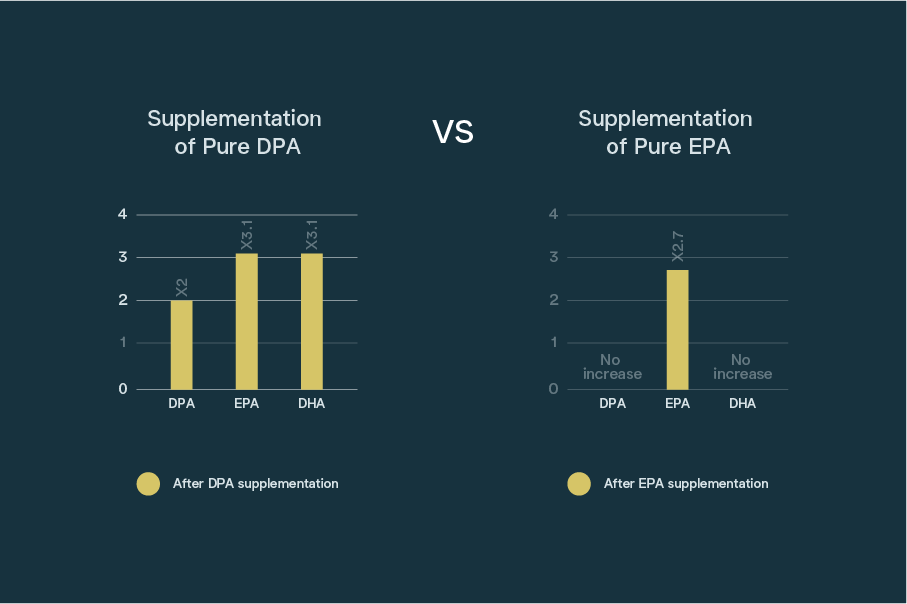
An interesting human clinical trial involved giving doses of concentrated DPA to a number of subjects. The study showed that, even after short-term supplementation with DPA, blood levels of EPA, DHA and DPA were all elevated. This study showed that unlike DPA, an EPA supplementation only increased the proportions of EPA in the body. This indicates DPA acts as a “storage depot,” allowing the body to store and access these crucial omega-3s as needed. This optimizes absorption and utilization.Miller E, Kaur G, Larsen A, Loh SP, Linderborg K, Weisinger HS, Turchini GM, Cameron-Smith D, Sinclair AJ. A short-term n-3 DPA supplementation study in humans. Eur J Nutr. 2013 Apr;52(3):895-904. doi: 10.1007/s00394-012-0396-3. Epub 2012 Jun 23. PMID: 22729967.
An earlier study by Kaur et al. (2009)Kaur G, Cameron-Smith D, Garg M, Sinclair AJ. Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-3): a review of its biological effects. Prog Lipid Res. 2011 Jan;50(1):28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.07.004. Epub 2010 Jul 23. PMID: 20655949. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20655949/ showed that supplementing with DPA significantly raised DPA concentrations in all tissues. It also significantly increased the concentration of DHA in liver and the concentration of EPA in liver, heart and skeletal muscles.